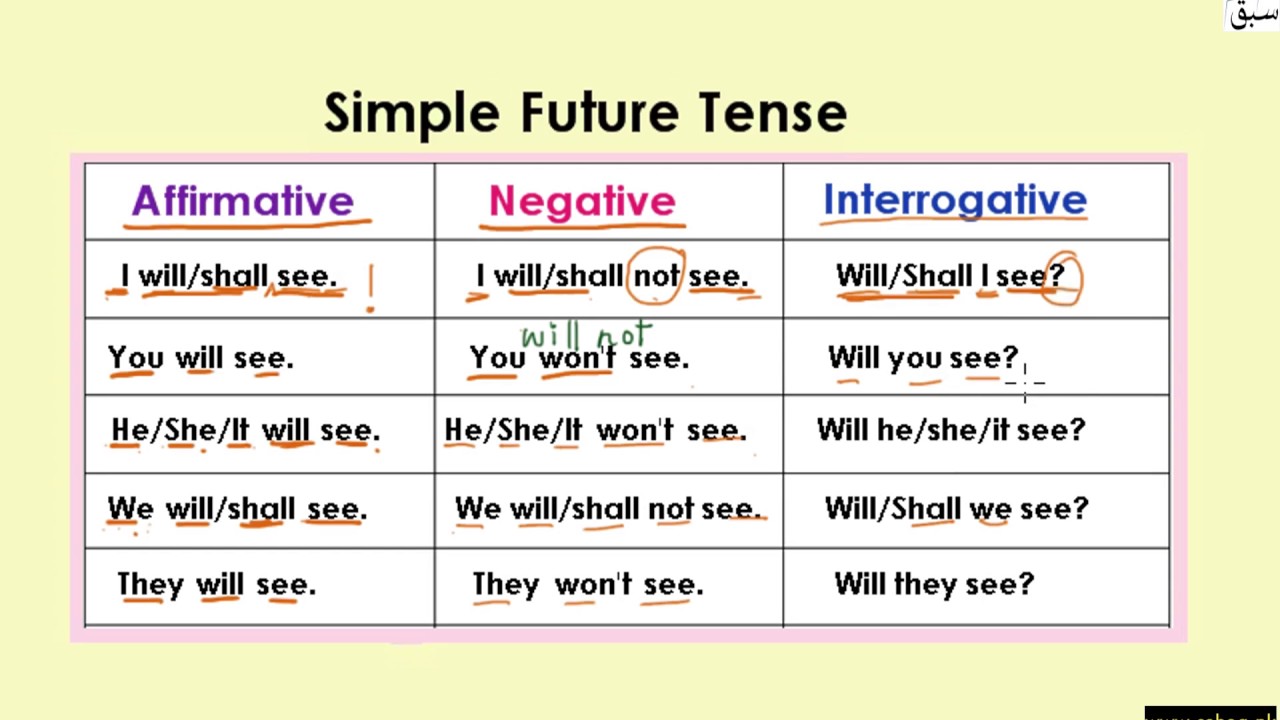
A. Future Perfect Continuous Tense Sentence Pattern
To make Future Perfect Continuous Tense sentences, you can use affirmative positive, negative and introgative sentence patterns as below.

B. Future Perfect Continuous Tense Sentences
After you know the pattern of forming affirmative positive, negative and introgative sentences from Future Perfect Continuous Tense, now it's time for friends to try to make the sentence Future Perfect Continuous Tense. Below, the author gives an example of the sentence Future Perfect Continuous Tense.
(+) He will have been studying at the university for two years by the end of this week
(-) He will not have been studying at the university for two years by the end of this week
(?) Will he have been studying at the university for two years by the end of this week?
C. Use of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
At the beginning of the explanation, the author has explained the use of Future Perfect Continuous Tense. Broadly speaking, these tenses are used to express a work that has begun in the past and will still be ongoing at a certain time in the future. Usually in sentences that use Future Perfect Continuous Tense, there is a description of the time period preceded by the word "for", for example: for two hours, for 3 months.
The addition of the statement of time period is intended to state that the incident is still ongoing or not yet completed and may continue. As shown in the example below:
I will have been living in Jakarta for three months by the end of September.
I will have been working for 3 hours by the end of twelve.
D. Time Description of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
When friends want to make a sentence Future Perfect Continuous Tense, friends can use time information, such as:
Sources
To make Future Perfect Continuous Tense sentences, you can use affirmative positive, negative and introgative sentence patterns as below.

B. Future Perfect Continuous Tense Sentences
After you know the pattern of forming affirmative positive, negative and introgative sentences from Future Perfect Continuous Tense, now it's time for friends to try to make the sentence Future Perfect Continuous Tense. Below, the author gives an example of the sentence Future Perfect Continuous Tense.
(+) He will have been studying at the university for two years by the end of this week
(-) He will not have been studying at the university for two years by the end of this week
(?) Will he have been studying at the university for two years by the end of this week?
C. Use of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
At the beginning of the explanation, the author has explained the use of Future Perfect Continuous Tense. Broadly speaking, these tenses are used to express a work that has begun in the past and will still be ongoing at a certain time in the future. Usually in sentences that use Future Perfect Continuous Tense, there is a description of the time period preceded by the word "for", for example: for two hours, for 3 months.
The addition of the statement of time period is intended to state that the incident is still ongoing or not yet completed and may continue. As shown in the example below:
I will have been living in Jakarta for three months by the end of September.
I will have been working for 3 hours by the end of twelve.
D. Time Description of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
When friends want to make a sentence Future Perfect Continuous Tense, friends can use time information, such as:
| By … Next year | By the end … | By the end of … Next … |
| By January next year | By the end of this week | By the end of January next year |
| By February next year | By the end of this month | By the end of February next year |
| By March next year | By the end of this year | By the end of March next year |
| By July next year | By the end of this summer | By the end of July next year |
Sources